Struggling with lower back pain? Don’t worry! Read my article to learn practical solutions to alleviate discomfort and get back on your feet with ease.
In recent years, low back pain (LBP) has become a major health issue around the world. This may be due to a changing work environment including the nature of long sitting work hours, especially in the booming information and technology (IT) and Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) industry.
Most people will experience it in their lifetime. Most people first encounter back pain between the ages of 30 and 50. This is partly due to the body’s changes with age. Pain often improves with rest, physical therapy, and medication. Reduce your risk of low back pain by maintaining a healthy weight and staying active.
Image Credit – https://pin.it/hgxP8BU
Today, I want to share my own story. A few days back, I lifted a heavy object and felt a sharp pain in my lower back. I couldn’t move without pain, and I worried I had done something serious. I spoke to the doctor, and he treated me for lower back pain.
Hence I decided to explore deeper into this for a better understanding of these conditions, their types, symptoms, and causes, I will share my knowledge in this article about how I recovered from this condition and went back to my normal life.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain refers to discomfort or pain in the region below the ribcage and above the hips.
Pain can range from mild to severe. In some cases, pain can make it difficult or impossible to walk, sleep, work, or do everyday activities.
Lower back pain improves with rest, pain relievers, and physical therapy (PT). Cortisone injections and hands-on treatments can relieve pain and help heal. Back injuries and conditions require surgical repair.

Types of LBP:
a. Acute LBP: comes on suddenly and lasts for a few weeks.
b. Chronic LBP: lasts more than 12 weeks or longer.
Symptoms of LBP:
LBP symptoms vary from person to person.
Some of the most common symptoms include:
• Pain when resting or sitting for long periods
• Pain when lifting something heavy or bending down
• Pain radiating from the hips
• Stiffness after inactivity or when first waking up
• Numbness or weakness
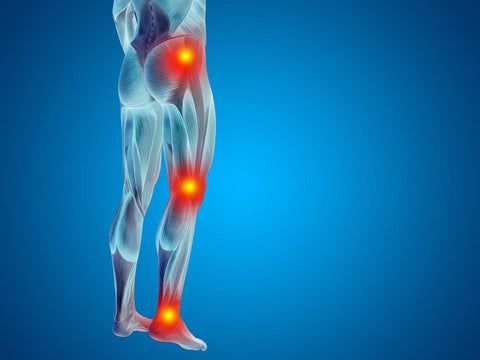
Radiating Pain down into legs. Image Credit – https://pin.it/6R6aU5l
There are other less common — but more severe — symptoms. They include:
• Pain in the legs or feet and the back
• Unintentional weight loss
• Fever
• Lack of bowel control
Consult a doctor if you experience severe symptoms or back pain lasting longer than 72 hours.
Causes of LBP
The causes of LBP can be varied. Some common causes include:
• Lifting heavy objects

• Poor posture
• Sitting for long periods

• Injury to the back
• Degenerative changes in the spine
• Medical conditions such as arthritis, osteoporosis, or cancer.
Is lower back pain common?
Most of the people around us experience it in their lifetime at some point. It’s one of the most common reasons people visit healthcare. Some of the risk factors for lower back pain include:
- Age: Most people over 30 have encountered back pain. Disc (the spongy soft cushions that separate the bones of the spine) wear with age. As the disc weakens and wear and tear down, pain and stiffness can result.
- Weight: People who are overweight /obese, are likely to have back pain. Excess weight puts pressure on joints and discs.
- Health: A weakened abdomen can make it difficult to support the spine, resulting in back strains and sprains. People who are excessive smokers and drinkers (alcohol) or live inactive lifestyles have a higher risk of back pain.
- Occupation: Jobs and activities that require heavy lifting or bending can increase the risk of a back injury.
- Structural problems: Severe back pain can result from conditions like scoliosis that change spine alignment.
- Disease: People, who have a family history of Osteoarthritis, may have a higher risk of lower back pain.
- Mental health: Depression and anxiety can cause back pain.
Diagnosis of lower back pain
A doctor will ask about your symptoms and conduct a thorough physical exam to determine where you’re feeling pain. The physical exam can also reveal whether pain affects your range of motion.
In addition, a doctor may check your reflexes and responses to certain sensations. This helps them determine if your lower back pain affects your nerves.
A doctor will likely monitor your condition for a few weeks before ordering additional tests unless your symptoms are concerning or you have a neurological loss. This is because most lower back pain resolves with simple self-care treatments.
Symptoms that require more testing include:
- weakness
- unintentional weight loss
- fever
- lack of bowel control
- pain radiates in the legs
You need to have immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms in addition to lower back pain.
Imaging tests
You may undergo imaging tests to check for:
- bone problems
- disc problems
- problems with the tendons and ligaments in your back
Imaging tests include:
- X-rays
- ultrasounds
- CT scans
- MRIs

Image – MRI Scan
Other tests
If a doctor suspects the bones in your back are weak, they may order a bone scan or bone density test.
Electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction tests can help a doctor identify any nerve problems.
Lower back pain treatment
Once you have received a diagnosis and understand what you’re dealing with, it’s time to create a treatment plan. Lower back pain usually improves with rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relievers. After a few days of rest, you can return to normal activities. Staying active increases blood flow to the area and helps you heal.
Other treatments for lower back pain depend on your symptoms and cause. They include:
Medications: Your doctor may recommend anti-inflammatory drugs or prescription drugs to relieve pain. Other medications relax muscles and prevent back spasms.
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen and improve your muscles’ flexibility so that they can support your spine and avoid other injuries.

Massage therapy: Massage therapy relaxes tight muscles, reduces pain, and restores normal function.
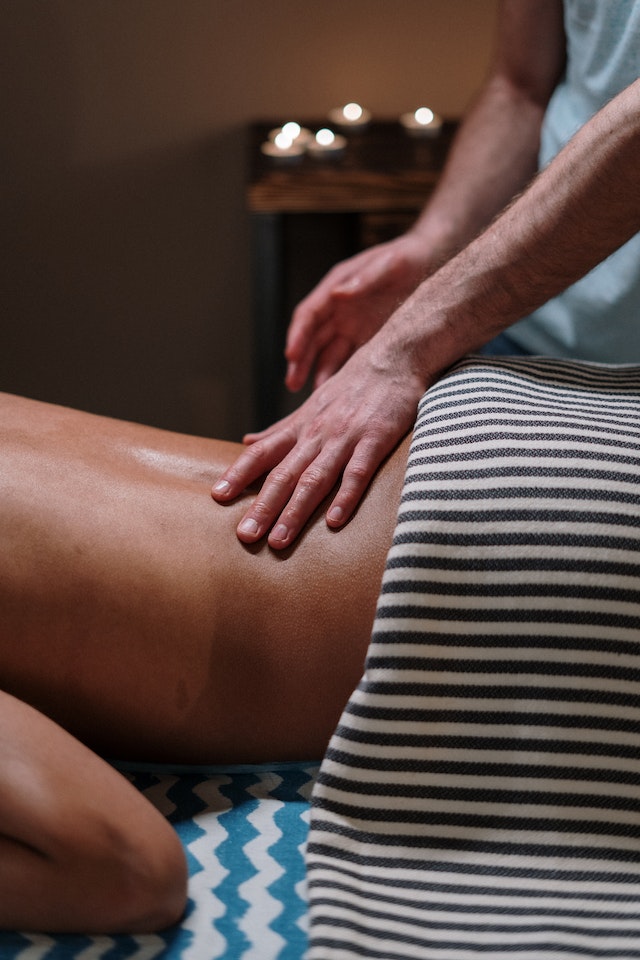
Injections: Your doctor might inject medication into your pain area. Steroid injections help reduce inflammation.
Surgery: Some injuries and conditions require surgical repair. Surgery is usually done when all other treatments fail.
Physical exercises to relieve LBP
Several physical exercises can relieve LBP. Some common exercises include:
a. Stretching exercises: Gentle stretching of the back and leg muscles can relieve tension and improve flexibility.
b. Core-strengthening exercises: By strengthening the back and abdominal muscles, LBP risk can be reduced.
c. Aerobic exercises: Activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling increase blood flow, strengthen muscles, and decrease pain.
d. Yoga: Incorporates stretching, breathing exercises, and postures that promote balance, strength, and relaxation.
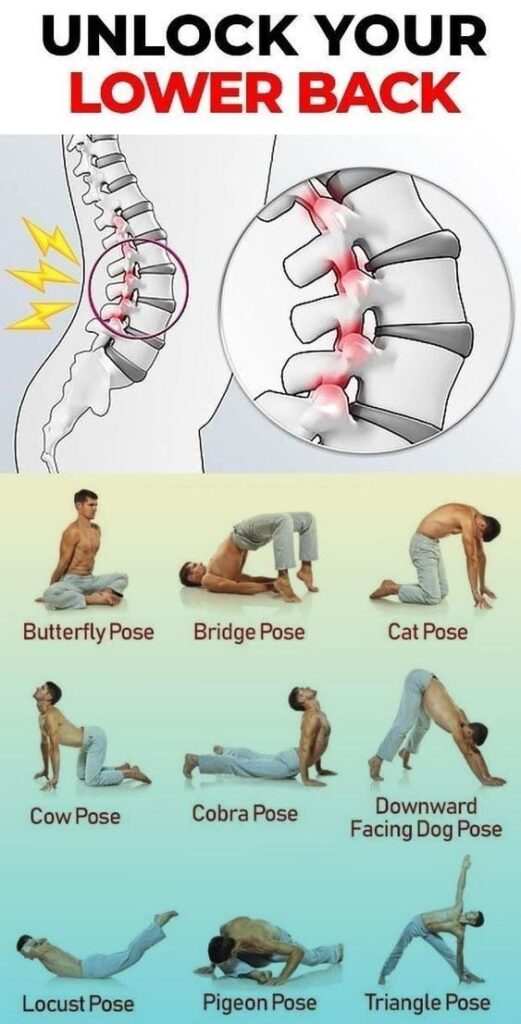
Image Credit – https://pin.it/PT3GJ28
Do’s and Don’ts for LBP
There are several things you can do to relieve LBP and prevent it from returning. These include:
- Maintain good posture and a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly and incorporate stretching into your routine.
- Don’t lift heavy objects improperly; use your legs, not your back.
- Don’t engage in high-impact activities that strain the back.
- Take breaks when sitting for long periods.
- Strengthen your core muscles.
- Manage stress levels, as stress can increase pain.

Image Credit – https://pin.it/iKThDad
Conclusion:
Lower back pain, while common, should not be taken lightly. It’s crucial to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatments to effectively manage and alleviate the pain and prevent it from returning. If you are experiencing LBP, it is best to see a doctor to rule out any serious medical conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are Herniated Discs and Slip Discs?
Herniated Discs: Occurs when the soft cushion-like material between spinal vertebrae bulges out, pressing nearby nerves and resulting in pain, numbness, or weakness in an arm or leg.
Slipped Discs: A slipped disc, also known as a bulging disk, occurs when a disk bulges out of place without breaking, and results in the same problem as a herniated disk.
Both conditions can contribute to LBP.
Is bed rest recommended for lower back pain?
While rest can help in the short term, prolonged bed rest can worsen LBP.
Gentle activities and exercises are often more beneficial.
Can obesity contribute to lower back pain?

Excessive weight can strain the lower back, leading to pain.
Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can alleviate LBP and reduce future risks.
Can lower back pain be prevented?
While not all LBP can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing proper posture and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk.
Can stress cause lower back pain?
Stress can contribute to muscle tension, which may result in lower back pain.
Engaging in stress-management techniques like meditation and relaxation exercises can alleviate symptoms.
How is LBP diagnosed?
The doctor diagnoses LBP based on your medical history and physical exam.
How long does LBP take to heal?
Healing duration varies depending on LBP cause and severity.
Acute LBP often resolves within a few weeks, while chronic LBP may require long-term management and lifestyle modifications.
What lifestyle changes can prevent LBP in the future?
Practicing a healthy posture, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly (with a focus on core strength), and using proper lifting techniques can help prevent future LBP episodes.
Additionally, avoiding prolonged sitting and incorporating regular breaks to stretch and move can benefit your lower back.